Registering Secrets
 Situation Analysis
Situation Analysis
As an operator, you may need to register secrets in VMware Secrets Manager so that your applications can securely access them.
This use case is about how to register secrets in VMware Secrets Manager.
 Screencast
Screencast
Here is a screencast that demonstrates this use case:
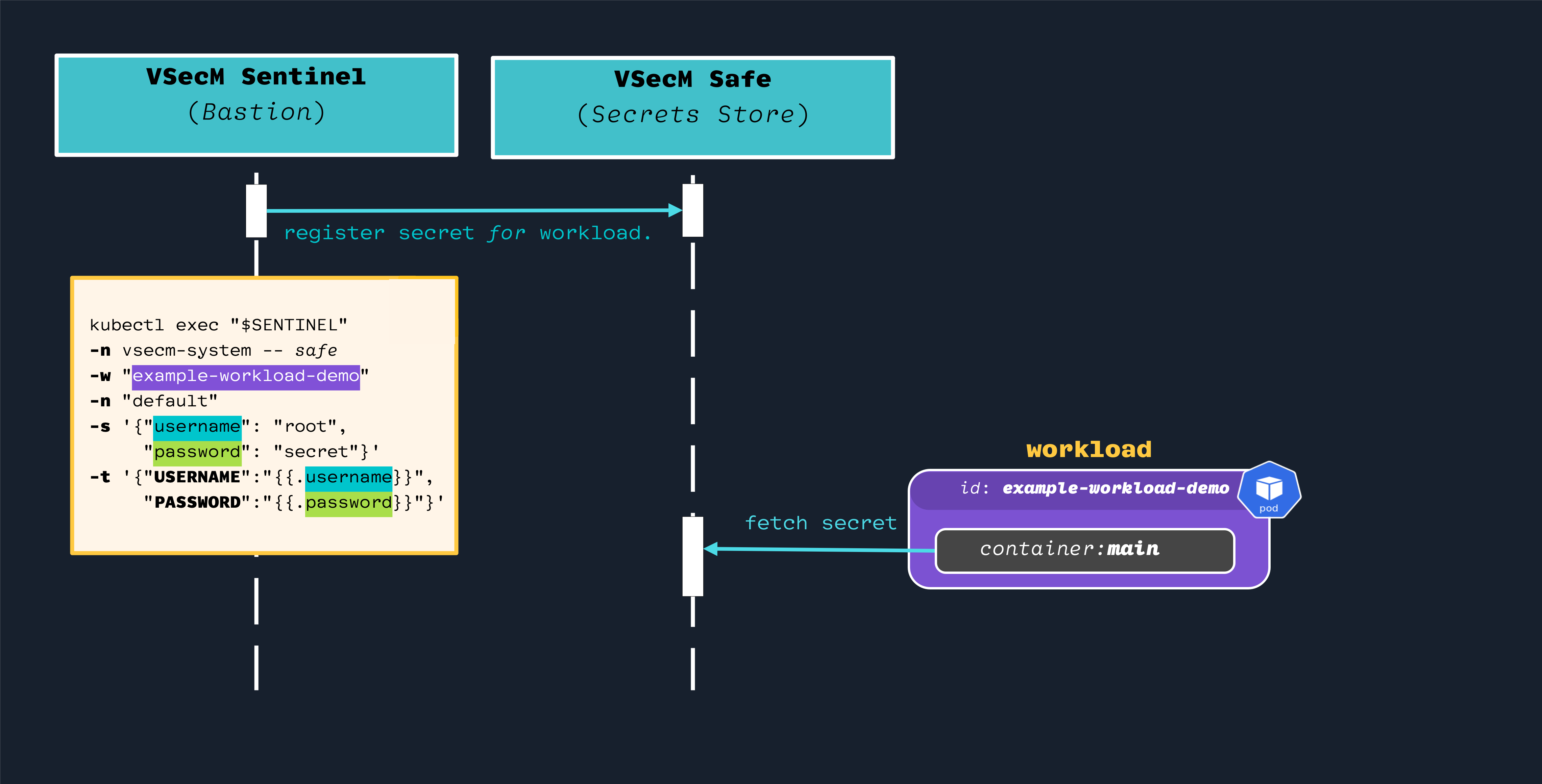
 High-Level Diagram
High-Level Diagram
Open the image in a new tab to see the full-size version:
 Implementation
Implementation
 Registering a Secret Using the CLI
Registering a Secret Using the CLI
To register a secret in VMware Secrets Manager, you can use the CLI as follows:
# $SENTINEL is the name of VSecM Sentinel pod.
kubectl exec "$SENTINEL" -n vsecm-system -- safe \
-w "example-workload-demo" \
-n "default" \
-s 'TopSecret!#'
Note that you don’t need to workload to be running to register a secret.
Here, -w is the workload name, -n is the namespace, and -s is the secret
value.
Check out the CLI reference for more details.
 Registering a Secret Using VSecM Sentinel Init Commands
Registering a Secret Using VSecM Sentinel Init Commands
VSecM Sentinel can also register secrets using init commands.
The best way to do this is to specify the init command values in its Helm chart values file.
Here is an example to register the same secret using the initCommand stanza
of values.yaml file:
# ./charts/sentinel/values.yaml
initCommand:
enabled: true
command: |
--
w:example-workload-demo
n:default
s:gen:TopSecret!#
--
There is a slightly-more-advanced “init command” example in [Mounting Kubernetes Secrets as Environment Variables][mounting-k8s-secrets] use case too.
[mounting-k8s-secrets]: /docs/use-case-mounting-secrets-as-env-vars/ “Mounting Kubernetes Secrets as Environment Variables
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Successfully registering secrets in VMware Secrets Manager is essential for ensuring secure and efficient access to sensitive data by your applications.
This guide provided two robust methods for registering secrets:
- using the Command Line Interface (CLI)
- and through VSecM Sentinel Init Commands.
Each method offers a streamlined approach tailored to different operational preferences and requirements.
Using the CLI, operators have the flexibility to directly execute commands within the Kubernetes environment, enabling immediate and precise secret registration. This method is particularly useful for those who prefer hands-on, scriptable interactions with their infrastructure.
Alternatively, the VSecM Sentinel Init Commands method integrates secret registration directly into the deployment process, offering a more automated and error-resistant approach by leveraging Helm chart configurations. This is advantageous for environments where automation and scalability are priorities.
Both methods are supported by detailed documentation and examples, ensuring that you have the necessary resources to implement the solution that best fits your operational needs.
By adopting these practices, you can enhance the security posture of your applications while maintaining a high level of operational efficiency.
 List of Use Cases in This Section
List of Use Cases in This Section
- Overview of Use Cases
- Registering Secrets
- Retrieving Secrets
- Using VSecM Sidecar
- Using VSecM SDK
- Using VSecM Init Container
- Encrypting Secrets
- Transforming Secrets
- Mounting Secrets as Volumes
- Mutating a Template File
- Encrypting Large Files
- Setting the Root Keys Externally
- Generating Pattern-Based Randomized Secrets
- VMware Secrets Manager Showcase